Food chain worksheet, an invaluable tool for exploring the intricate tapestry of life, offers a captivating journey into the interconnectedness of ecosystems. Through its interactive and engaging format, this worksheet empowers learners to unravel the complex dynamics that govern the flow of energy and the delicate balance of nature.
From the foundational components of a food chain to the fascinating interplay of food webs, this worksheet delves into the heart of ecological processes. It illuminates the vital roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers, while unraveling the intricate hierarchy of trophic levels and the significance of food pyramids.
Human Impact on Food Chains: Food Chain Worksheet
Human activities can have a significant impact on food chains, disrupting the delicate balance that exists between different species and their environments. Habitat loss, pollution, and overfishing are among the primary factors contributing to these disruptions.
Habitat Loss
Habitat loss occurs when natural areas are converted to other uses, such as agriculture, urbanization, or mining. This can have devastating consequences for wildlife, as it reduces the availability of food, shelter, and breeding grounds. When a species loses its habitat, it can lead to a decline in its population and potentially even extinction.
Pollution
Pollution can enter food chains through various sources, including industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and vehicle emissions. Pollutants can accumulate in the tissues of organisms, affecting their health and reproductive success. For example, pesticides can kill insects that are important food sources for birds, while heavy metals can accumulate in fish and shellfish, posing a risk to human health.
Overfishing, Food chain worksheet
Overfishing occurs when fish are harvested at a rate faster than they can reproduce. This can lead to a decline in fish populations, disrupting food chains and affecting species that rely on fish as a food source. For instance, overfishing of sharks can disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems, as sharks play a crucial role in regulating prey populations.
Importance of Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are essential in preserving food chains and mitigating the impacts of human activities. These efforts include protecting and restoring habitats, reducing pollution, and implementing sustainable fishing practices. By conserving food chains, we can help ensure the survival of species and maintain the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Food Chain Models
Food chain models are simplified representations of food chains that help scientists understand and analyze the complex interactions between organisms in an ecosystem. These models can take various forms, each with its own advantages and limitations.
Types of Food Chain Models
There are two main types of food chain models:
- Linear Food Chains:Represent a simple, one-way flow of energy from producers to consumers. Each organism feeds on the one below it in the chain.
- Food Webs:More complex models that represent the interconnected feeding relationships within an ecosystem. Organisms can have multiple food sources and predators, creating a network of interactions.
Interactive Food Chain Worksheet
Interactive food chain worksheets are a great way for students to learn about food chains and how they work. These worksheets allow students to explore and manipulate different food chains, and they can be used as a starting point for discussions about the importance of food chains in the environment.
Instructions for Using the Worksheet
- Start by choosing a food chain from the list provided.
- Once you have chosen a food chain, click on the “Start” button.
- The worksheet will then open in a new window.
- You can use the worksheet to explore the food chain by clicking on the different organisms.
- You can also use the worksheet to manipulate the food chain by dragging and dropping the organisms into different positions.
- When you are finished exploring the food chain, click on the “Finish” button.
Sample Food Chain
The following is a sample food chain that you can use to get started:
- Grass
- Grasshopper
- Snake
- Hawk
Food Chain Simulation
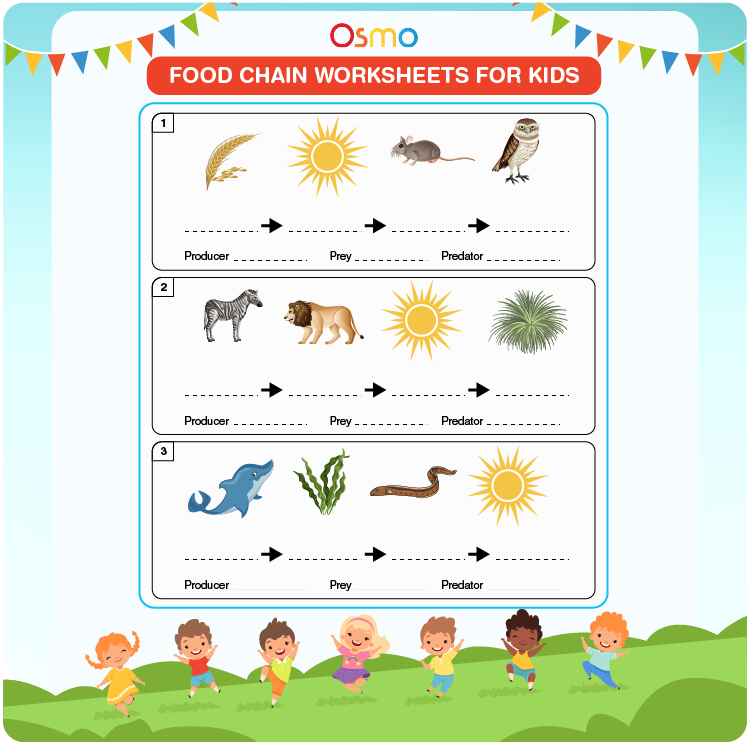

A food chain simulation is a computer model that represents the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem. It allows users to explore how changes in the environment, such as the addition or removal of a species, can affect the stability of the ecosystem.
To use a food chain simulation, users typically select a species from a list of available organisms. They can then add or remove species from the simulation and observe how the changes affect the population sizes of other species. Some simulations also allow users to change environmental factors, such as the amount of sunlight or the temperature.
Sample Scenario
One common scenario used in food chain simulations is the removal of a top predator. In a natural ecosystem, top predators play an important role in regulating the populations of their prey. When a top predator is removed, the populations of its prey can increase, which can in turn lead to a decrease in the populations of the prey’s prey.
This can have a ripple effect throughout the entire ecosystem.
Food Chain Case Studies
Food chains are intricate ecosystems that can be disrupted by a variety of factors. These disruptions can have cascading effects on the entire food chain, from the smallest organisms to the largest predators.
By examining real-world case studies, we can learn about the impacts of these disruptions and the lessons that can be learned from them.
DDT and the Peregrine Falcon
One of the most well-known examples of a food chain disruption is the impact of DDT on the peregrine falcon. DDT is a pesticide that was widely used in the 1950s and 1960s to control insects.
DDT accumulates in the fatty tissues of animals, and when birds of prey eat contaminated prey, they can accumulate high levels of DDT in their bodies. This can lead to eggshell thinning, which makes the eggs more likely to break during incubation.
As a result of DDT contamination, peregrine falcon populations declined dramatically in the 1960s and 1970s. In the United States, the peregrine falcon was listed as an endangered species in 1970.
The ban on DDT in the United States in 1972 helped to protect peregrine falcons, and the population has since rebounded. However, DDT is still used in some other countries, and it continues to pose a threat to birds of prey.
The DDT and peregrine falcon case study is a reminder of the importance of understanding the potential impacts of pesticides and other chemicals on wildlife.
Additional Resources:
FAQ Corner
What is the importance of food chains?
Food chains play a crucial role in maintaining the stability and balance of ecosystems. They ensure the transfer of energy and nutrients throughout the ecosystem, supporting the survival and growth of all organisms.
How do food webs differ from food chains?
Food webs are more complex representations of ecological interactions compared to food chains. They illustrate the interconnectedness of multiple food chains within an ecosystem, highlighting the diverse feeding relationships and the flow of energy among different species.
What are the different types of food chains?
There are various types of food chains, including terrestrial food chains (occurring on land), aquatic food chains (occurring in water bodies), and detrital food chains (based on the decomposition of organic matter).
