Food exchanges are thriving platforms where individuals come together to share their culinary creations, foster connections, and promote healthier eating habits. As a vibrant tapestry of flavors and experiences, these exchanges offer a myriad of benefits, ranging from nutritional nourishment to social well-being.
From community-organized potlucks to online marketplaces, food exchanges encompass a diverse spectrum of formats. Whether you’re a seasoned chef eager to showcase your culinary prowess or a novice cook seeking inspiration, these platforms provide a welcoming space for all.
Food Exchanges
Food exchanges are events where individuals gather to exchange homemade or locally sourced food items. These exchanges provide opportunities for participants to share their culinary creations, support local farmers and artisans, and connect with their community over a shared love of food.The
purpose of food exchanges is to foster a sense of community and promote sustainable food practices. By exchanging homemade goods, participants reduce waste and support local businesses. Food exchanges also encourage participants to experiment with new recipes and ingredients, broadening their culinary horizons.
Benefits of Participating in Food Exchanges
Participating in food exchanges offers numerous benefits, including:
- Community building:Food exchanges provide a platform for individuals to connect with their neighbors and foster a sense of community.
- Support for local farmers and artisans:By purchasing homemade or locally sourced food items, participants support local businesses and promote sustainable food practices.
- Reduced food waste:Food exchanges help reduce food waste by providing a platform for individuals to exchange excess or unwanted food items.
- Culinary exploration:Food exchanges encourage participants to experiment with new recipes and ingredients, broadening their culinary horizons.
Types of Food Exchanges
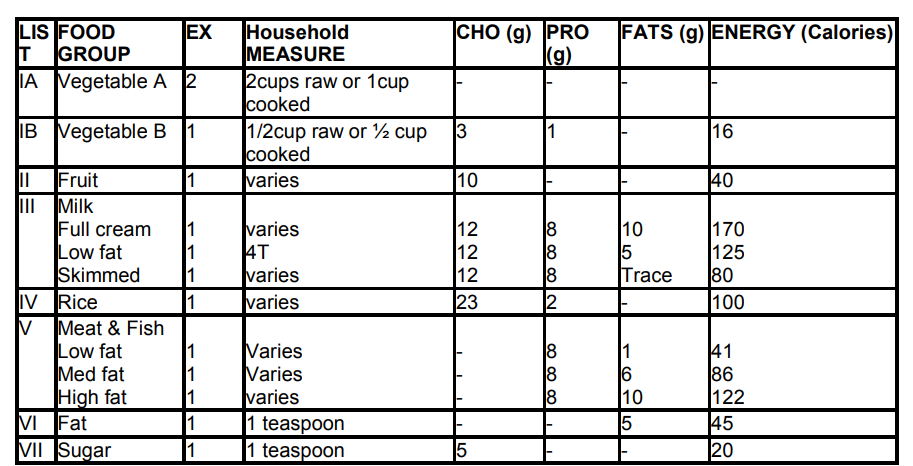
Food exchanges are a system of classifying foods into groups based on their nutrient content. This system helps people with diabetes plan their meals and manage their blood sugar levels. There are three main types of food exchanges: carbohydrate, protein, and fat.
Carbohydrate Exchanges
Carbohydrate exchanges are foods that contain carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. One carbohydrate exchange contains 15 grams of carbohydrates.
- Examples of carbohydrate exchanges include:
- 1 slice of bread
- 1/2 cup of cooked pasta
- 1 cup of fruit
- 1 cup of nonfat milk
Advantages of carbohydrate exchanges:
- Easy to understand and use
- Helps people with diabetes control their blood sugar levels
Disadvantages of carbohydrate exchanges:
- Does not take into account the glycemic index of foods
- Can be restrictive for people who need to limit their carbohydrate intake
Protein Exchanges
Protein exchanges are foods that contain protein. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues. One protein exchange contains 7 grams of protein.
- Examples of protein exchanges include:
- 1 ounce of meat
- 1/2 cup of cooked beans
- 1 cup of nonfat yogurt
- 1 egg
Advantages of protein exchanges:
- Helps people with diabetes control their blood sugar levels
- Provides essential nutrients
Disadvantages of protein exchanges:
- Can be difficult to track for people who need to limit their protein intake
- Can be expensive
Fat Exchanges
Fat exchanges are foods that contain fat. Fat is essential for energy storage and insulation. One fat exchange contains 5 grams of fat.
- Examples of fat exchanges include:
- 1 teaspoon of oil
- 1 tablespoon of butter
- 1/4 avocado
- 1 ounce of nuts
Advantages of fat exchanges:
- Provides essential nutrients
- Helps people with diabetes control their blood sugar levels
Disadvantages of fat exchanges:
- Can be high in calories
- Can be difficult to track for people who need to limit their fat intake
How to Participate in Food Exchanges
Participating in food exchanges offers a unique and rewarding way to connect with fellow food enthusiasts, share culinary creations, and discover new flavors. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to get started:
Finding Food Exchanges
* Online Directories:Websites such as Food Exchange Network and Food Swap Directory provide listings of active food exchanges in different regions.
Local Community Centers
Many community centers and recreation departments host food exchanges as part of their programming.
Social Media
Join Facebook groups and follow food exchange-related accounts to stay informed about upcoming events.
Joining a Food Exchange
* Contact the Organizer:Once you’ve found a food exchange you’re interested in, reach out to the organizer via email or phone to inquire about membership requirements.
Meet Attendance Criteria
Most food exchanges have specific attendance requirements, such as a minimum number of events attended per year.
Pay Membership Fees
Some food exchanges charge a small annual membership fee to cover administrative costs.
Tips for Participating in Food Exchanges
* Prepare Delicious Dishes:Showcase your culinary skills by preparing dishes that reflect your passion for food. Consider the theme of the exchange and the preferences of other participants.
Share Recipes
Provide written or digital copies of your recipes so that others can recreate your creations at home.
Engage with Participants
Food exchanges are social events, so make an effort to connect with fellow members, share stories, and learn about their culinary interests.
Follow Exchange Guidelines
Respect the rules and guidelines established by the food exchange organizer, such as food safety regulations and the exchange format.
Have Fun
The most important aspect of participating in food exchanges is to enjoy the experience, connect with others, and savor the culinary delights on offer.
Benefits of Food Exchanges
Food exchanges offer a wealth of benefits, both nutritional and social. They provide a structured approach to meal planning, ensuring a balanced intake of essential nutrients.
Nutritional Benefits
- Improved Diet Quality:Exchanges guide individuals toward nutrient-rich foods from all food groups, promoting a healthier overall diet.
- Calorie Control:Exchanges assign specific calorie values to foods, helping participants manage their calorie intake and maintain a healthy weight.
- Dietary Variety:Exchanges encourage the consumption of a wide range of foods, reducing the risk of nutrient deficiencies and promoting a balanced intake.
Social Benefits
- Support and Motivation:Exchanges provide a sense of community and support, as participants connect with others who are also working towards their dietary goals.
- Accountability:Exchanges require participants to track their food intake, promoting self-awareness and accountability.
- Education and Empowerment:Exchanges teach participants about nutrition and healthy eating habits, empowering them to make informed food choices.
Success Stories
Numerous individuals have experienced significant benefits from participating in food exchanges. For example, one participant lost over 50 pounds and improved their overall health by following an exchange-based diet.
Challenges of Food Exchanges

Participating in food exchanges can be a rewarding experience, but it can also present some challenges. These challenges can include finding the right exchange partner, agreeing on terms, and ensuring that the food is safe and of good quality.
One of the biggest challenges of food exchanges is finding the right exchange partner. You need to find someone who is willing to exchange food with you, and who has food that you are interested in. You also need to find someone who is reliable and trustworthy, and who will follow through on their commitments.
Another challenge of food exchanges is agreeing on terms. You need to decide how much food you will exchange, what types of food you will exchange, and when and where you will exchange the food. You also need to decide how you will handle any disputes that may arise.
Finally, you need to ensure that the food you exchange is safe and of good quality. You should inspect the food carefully before you eat it, and you should only eat food that you are confident is safe.
Overcoming the Challenges of Food Exchanges
There are a few things you can do to overcome the challenges of food exchanges. First, you can start by getting to know your potential exchange partners. Talk to them about their interests, their food preferences, and their availability. This will help you determine if they are a good fit for an exchange.
Once you have found a potential exchange partner, you should discuss the terms of the exchange in detail. Make sure you agree on how much food you will exchange, what types of food you will exchange, and when and where you will exchange the food.
You should also discuss how you will handle any disputes that may arise.
Finally, you should always inspect the food you receive from an exchange partner before you eat it. Make sure the food is fresh and of good quality, and that it has been stored properly.
Resources for Overcoming the Challenges of Food Exchanges
There are a number of resources available to help you overcome the challenges of food exchanges. These resources include:
- The Food Exchange Network: The Food Exchange Network is a website that connects people who are interested in exchanging food. The website provides a directory of exchange partners, as well as tips and advice on how to participate in food exchanges.
- Local food co-ops: Local food co-ops are often a good place to find exchange partners. Food co-ops are typically run by members, and they often have a strong sense of community. This can make it easier to find exchange partners who are reliable and trustworthy.
- Community gardens: Community gardens are another good place to find exchange partners. Community gardens are typically run by volunteers, and they often have a strong sense of community. This can make it easier to find exchange partners who are reliable and trustworthy.
Food Exchange Resources

This section provides resources for finding food exchanges, learning more about them, and getting help with them.
Resources for Finding Food Exchanges
The following resources can help you find food exchanges in your area:
- Local food banks and pantries
- Community centers
- Religious organizations
- Online directories of food exchanges
Resources for Learning More About Food Exchanges
The following resources can help you learn more about food exchanges:
- Websites of food exchange organizations
- Articles and blog posts about food exchanges
- Books about food exchanges
Resources for Getting Help with Food Exchanges
The following resources can help you get help with food exchanges:
- Local food banks and pantries
- Community centers
- Religious organizations
- Government agencies
Expert Answers
What are the different types of food exchanges?
Food exchanges encompass a wide range of formats, including community potlucks, online marketplaces, and subscription-based services.
What are the benefits of participating in food exchanges?
Food exchanges offer numerous benefits, such as access to diverse cuisines, opportunities for social interaction, and the promotion of healthy eating habits.
How can I find food exchanges in my area?
You can find food exchanges by searching online directories, contacting local community centers, or joining social media groups dedicated to food sharing.