PCO foods are a crucial part of managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. By understanding the relationship between PCOS and diet, you can make informed choices about the foods you eat to improve your overall health and well-being.
PCOS is characterized by insulin resistance, which can lead to weight gain, irregular periods, and fertility issues. PCO foods are designed to help manage insulin resistance and improve PCOS symptoms. These foods are typically low in glycemic index, meaning they release sugar slowly into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in insulin levels.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and PCO Foods

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by irregular periods, high levels of androgens (male hormones), and the presence of cysts on the ovaries. PCOS can also lead to a number of other health problems, including insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
Diet plays an important role in managing PCOS. Eating a healthy diet can help to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce androgen levels, and promote regular ovulation. Some of the best foods for women with PCOS include:
Low-glycemic index foods
Low-glycemic index (GI) foods are foods that release sugar slowly into the bloodstream. This helps to prevent spikes in insulin levels, which can worsen PCOS symptoms. Some good low-GI foods include:
- Whole grains
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Legumes
- Lean protein
Fiber-rich foods, Pco foods
Fiber is another important nutrient for women with PCOS. Fiber helps to slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream and can help to improve insulin sensitivity. Some good sources of fiber include:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Legumes
- Nuts
- Seeds
Anti-inflammatory foods
Inflammation is a major contributing factor to PCOS. Eating anti-inflammatory foods can help to reduce inflammation and improve PCOS symptoms. Some good anti-inflammatory foods include:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Fatty fish
- Olive oil
- Nuts
- Seeds
Nutrient Considerations for PCO Foods
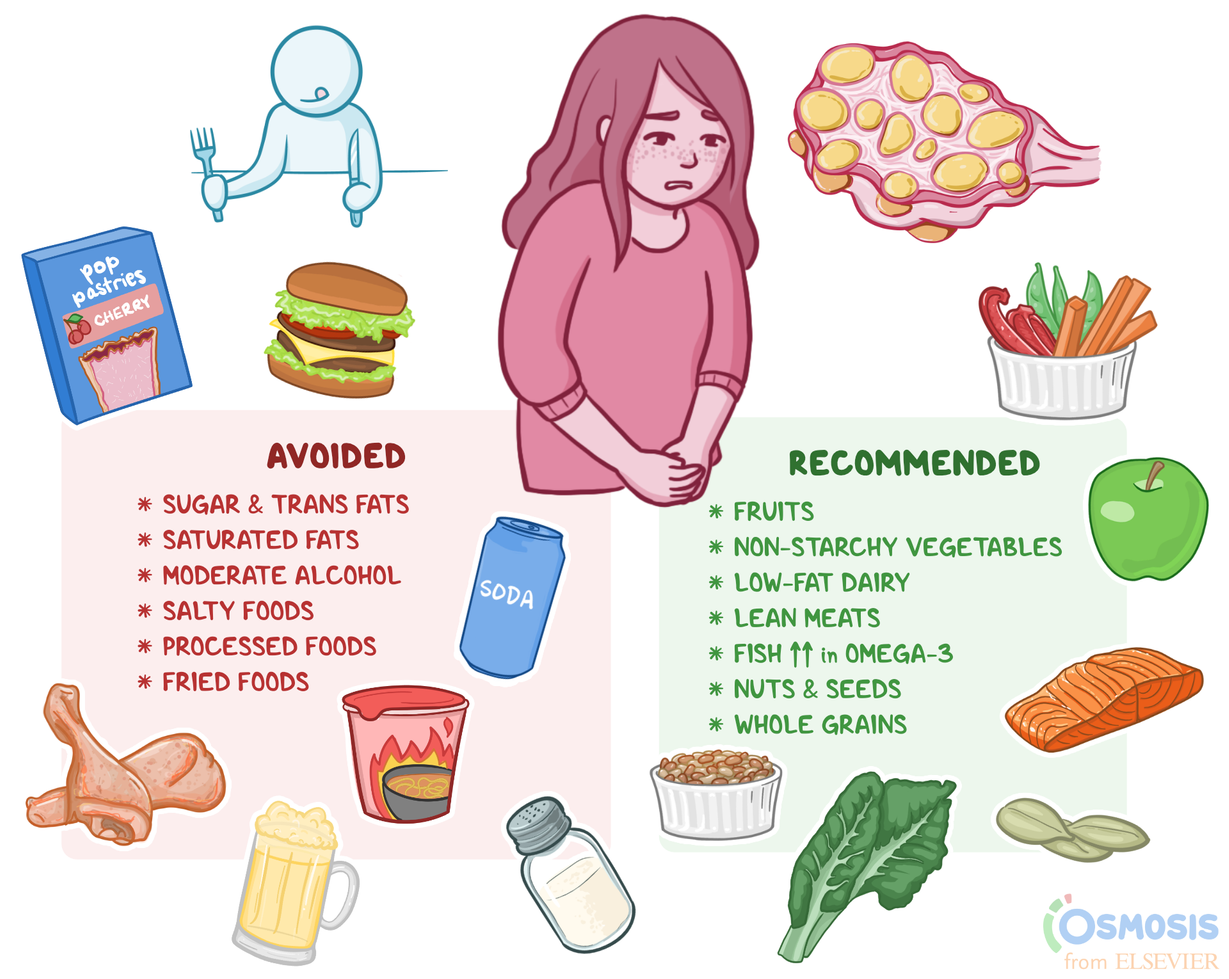
Understanding the nutritional needs of individuals with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is crucial for managing the condition effectively. PCO foods should prioritize a balanced macronutrient and micronutrient composition to support overall well-being and address PCOS-related symptoms.
Macronutrient Balance
Macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, play a vital role in managing PCOS. Maintaining a balance among these macronutrients helps regulate blood sugar levels, promote satiety, and support hormone production.
- Carbohydrates:Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, provide sustained energy without causing blood sugar spikes. They also support fiber intake, which is important for managing insulin sensitivity.
- Protein:Protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, and legumes, help regulate appetite, promote muscle mass, and support hormone production. Adequate protein intake is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and managing PCOS symptoms.
- Fats:Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, support hormone production, reduce inflammation, and promote satiety. Including healthy fats in the diet can help balance blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are essential for overall health and well-being. In the context of PCOS, certain micronutrients play specific roles:
- Vitamin D:Vitamin D deficiency is common in individuals with PCOS. Vitamin D supports hormone production, insulin sensitivity, and inflammation reduction.
- Magnesium:Magnesium is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body. Adequate magnesium intake supports hormone production, reduces inflammation, and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Zinc:Zinc is essential for hormone production, immune function, and insulin sensitivity. Zinc deficiency is associated with increased PCOS symptoms.
Meal Planning with PCO Foods

Meal planning is crucial for managing PCOS. By incorporating PCO-friendly foods into your diet, you can help regulate your hormones, reduce inflammation, and improve insulin sensitivity.
Guidelines for Meal Planning
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods:Fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains should form the foundation of your meals.
- Include PCO-friendly foods:Foods rich in fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants, such as leafy greens, berries, fatty fish, and nuts, can help manage PCOS symptoms.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats:These foods can worsen inflammation and insulin resistance.
- Control portion sizes:Eating smaller portions can help manage blood sugar levels and prevent overeating.
- Eat regular meals:Eating every 3-4 hours can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce cravings.
Sample Meal Plans
Here are some sample meal plans that demonstrate how to balance PCO foods throughout the day:
| Meal | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Snacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Oatmeal with berries and nuts | Grilled salmon salad with quinoa | Chicken stir-fry with brown rice | Apple with peanut butter |
| Day 2 | Yogurt with fruit and granola | Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread | Baked fish with roasted vegetables | Trail mix with seeds and nuts |
| Day 3 | Smoothie with spinach, banana, and almond milk | Tuna sandwich on whole-wheat bread | Spaghetti squash with meat sauce | Hummus with carrot sticks |
Importance of Portion Control and Meal Frequency
Portion control and meal frequency are essential for managing PCOS. Eating smaller portions helps prevent overeating and blood sugar spikes. Eating regular meals throughout the day helps regulate blood sugar levels, reduce cravings, and improve insulin sensitivity.
Lifestyle Modifications and PCO Foods
In addition to dietary modifications, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing PCOS. Exercise and stress management complement PCO foods in promoting hormonal balance, reducing inflammation, and improving overall well-being.
Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits for individuals with PCOS, including:
- Enhanced insulin sensitivity:Exercise improves the body’s ability to use insulin, reducing insulin resistance and blood sugar levels.
- Reduced androgen production:Physical activity helps lower androgen levels, which can lead to improved hormonal balance.
- Weight management:Exercise promotes weight loss, which can reduce the severity of PCOS symptoms and improve fertility.
- Improved mood:Physical activity releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects and can reduce stress.
Role of Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress can worsen PCOS symptoms by disrupting hormonal balance and increasing inflammation. Incorporating stress reduction techniques into your lifestyle can help mitigate these effects.
- Mindfulness:Practicing mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce stress and improve emotional well-being.
- Deep breathing exercises:Deep breathing exercises can help calm the nervous system and reduce stress levels.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT):CBT is a type of therapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to stress.
By combining PCO foods with lifestyle modifications such as exercise and stress management, individuals with PCOS can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their overall health and well-being.
FAQ Overview
What are the benefits of eating PCO foods?
PCO foods can help manage insulin resistance, improve PCOS symptoms, and support overall health and well-being.
What are some examples of PCO foods?
PCO foods include lean protein, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
How can I incorporate PCO foods into my diet?
You can incorporate PCO foods into your diet by creating meal plans that include these foods throughout the day. It’s also important to focus on portion control and meal frequency.
